Trams in Mainz
| Mainz tramway network | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 GT6M tram at Mainz Hauptbahnhof, 2009. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Locale | Mainz, Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Mainz tramway network (German: Straßenbahnnetz Mainz) is a network of tramways forming part of the public transport system in Mainz, the capital city of the federal state of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Opened in 1883, the network has been operated since 2001 by the Mainzer Verkehrsgesellschaft (MVG), and is integrated in the Rhein-Main-Verkehrsverbund (RMV).
Lines
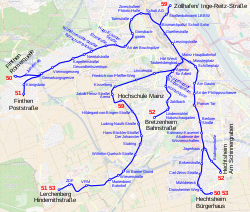
[edit]As of 2017[update], the Mainz tramway network has the following five lines:
| Line | Route |
|---|---|
| 50 | Hechtsheim/Bürgerhaus ↔ Hechtsheim/Mühldreieck ↔ Hechtsheim/Jägerhaus ↔ Mainz/Pariser Tor ↔ Mainz/Hauptbahnhof ↔ Mombach/Turmstraße (Haltepunkt Waggonfabrik) ↔ Gonsenheim/Kapellenstraße ↔ Finthen/Gemarkungsgrenze ↔ Finthen/Römerquelle |
| 51 | Finthen;↔ Mainz/Hauptbahnhof ↔ Hauptbahnhof West;↔ Universität;↔ Lerchenberg;↔ (launched: 2016) |
| 52 | Hechtsheim/Am Schinnergraben ↔ Hechtsheim/Jägerhaus ↔ Mainz/Pariser Tor ↔ Mainz/Hauptbahnhof ↔ Mainz/Zahlbach ↔ Bretzenheim/Bahnstraße |
| 53 | Hechtsheim/Bürgerhaus ↔ Hechtsheim/Mühldreieck ↔ Hechtsheim/Jägerhaus ↔ Mainz/Pariser Tor ↔ Mainz/Hauptbahnhof ↔ Universität ↔ Lerchenberg |
| 59 | Zollhafen ↔ Bismarckplatz ↔ Mainz Hauptbahnhof ↔ Hauptbahnhof West ↔ Hochschule Mainz (launched: 2017) |
Since Autumn 2016, the "Mainzelbahn" has been transporting passengers from Hauptbahnhof West (main station, west entrance) via University and Marienborn to Lerchenberg, and offers a fast connection between the main station and the University as well as the headquarters of ZDF ("Zweites Deutsches Fernsehen", a public television channel in Germany) in the district of Lerchenberg. Further, a new line is planned. The "Zollhafen Tram" links the new Zollhafen residential area with the tram network. To operate the new lines, the MVG ordered 10 Variotrams from Stadler Rail.[1]
Rolling stock
[edit]| Manufacturer | Type | Quantity | Numbers | built in | low-floor vehicle | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duewag / Siemens | M8S | 1 | 277 | 1975 | no | Bought in 1987/89 from Bielefeld Stadtbahn; Identical vehicles 278-280 were scrapped in 2016. |
| Duewag / Siemens | M8C | 6 | 271–276 | 1984 | no | Modernised at Ceglec in Prague between 2015 and 2017. |
| Adtranz | GT6M-ZR | 16 | 201–216 | 1996 | yes | |
| Stadler Rail | Variobahn | 9 | 217–225 | 2011/12 | yes | |
| 10 | 227-236 | 2015/16 | yes | Ten further trams for operating the new Mainzelbahn and Zollhafen line. |
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- Herbst, Günther (2008). 125 Jahre Mainzer Straßenbahn 1883 – 2008: Die letzten 14 Jahre 1994 – 2008 [125 Years Mainz Tramway 1883 – 2008: the last 14 years 1994 – 2008] (in German).
- Huber, Wilhelm (2002). Das Mainz-Lexicon [The Mainz-Lexicon] (in German). Mainz: Verlag Hermann Schmidt. ISBN 3-87439-600-2.
- Kochems, Michael; Höltge, Dieter (2011). Straßen- und Stadtbahnen in Deutschland [Tramways and Stadtbahnen in Germany] (in German). Vol. Band 12: Rheinland-Pfalz/Saarland [Volume 2: Rhineland-Palatinate/Saarland]. Freiburg i. B., Germany: EK-Verlag. ISBN 9783882553932.
- Neise, Harald (1983). Mainz und seine Straßenbahn 1883 – 1983 [Mainz and its Tramway 1883 – 1983] (in German). Kohlhammer Verlag.
- Neise, Harald (1994). 111 Jahre Mainzer öffentlicher Personennahverkehr 1883 – 1994 [111 Years Mainz local public transport 1883 – 1994] (in German).
- Neise, Harald; Weismüller, Dirk, eds. (3 July 2004). Wenn der Funke überspringt [When the sparks jump!] (in German). Mainz: Mainzer Verkehrsgesellschaft mbH.
- Schwandl, Robert (2012). Schwandl's Tram Atlas Deutschland (in German and English) (3rd ed.). Berlin: Robert Schwandl Verlag. pp. 100–101. ISBN 9783936573336.
External links
[edit]![]() Media related to Trams in Mainz at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Trams in Mainz at Wikimedia Commons
- Mainz database / photo gallery and Mainz tram list at Urban Electric Transit – in various languages, including English.
- Mainz database / photo gallery at Phototrans – in various languages, including English.